Document-oriented database products
37,739 Companies
What is Document-oriented database?
A document-oriented database, or document store, is a computer program designed for storing, retrieving and managing document-oriented information, also known as semi-structured data. Document-oriented databases are one of the main categories of NoSQL databases, and the popularity of the term "document-oriented database" has grown with the use of the term NoSQL itself. XML databases are a subclass of document-oriented databases that are optimized to work with XML documents. Graph databases are similar, but add another layer, the relationship, which allows them to link documents for rapid traversal. Document-oriented databases are inherently a subclass of the key-value store, another NoSQL database concept. The difference lies in the way the data is processed; in a key-value store the data is considered to be inherently opaque to the database, whereas a document-oriented system relies on internal structure in the document in order to extract metadata that the database engine uses for further optimization.
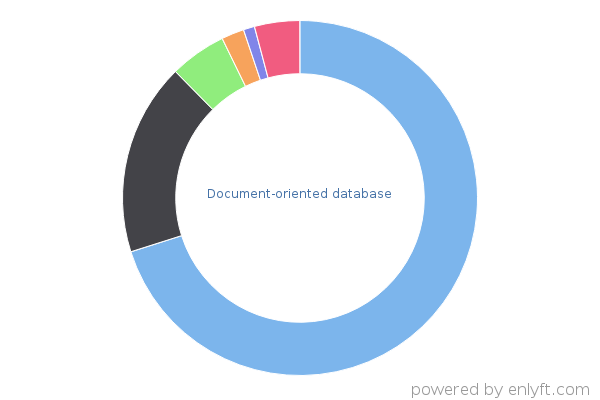
Market Share of Document-oriented database products
At enlyft, we use sophisticated, patent-pending algorithms to track the use of various Document-oriented database products and technologies. We track 15 products in the Document-oriented database category, and have found 37,739 companies using these products.

Target customers using Document-oriented database products to accomplish your sales and marketing goals.
| Product |
Install base
# of companies we found using this product |
Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| DynamoDB | 26,014 | 68% |
| Azure Cosmos DB | 6,905 | 18% |
| Altova MissionKit | 1,845 | < 5% |
| RavenDB | 694 | < 5% |
| Oracle Coherence | 673 | < 5% |
| Azure Table Storage | 621 | < 5% |
| Apache Parquet | 442 | < 5% |
| RethinkDB | 298 | < 5% |
| ArangoDB | 105 | < 5% |
| TokuMX | 40 | < 5% |
| eXistdb | 37 | < 5% |
| Amazon WorkDocs | 30 | < 5% |
| BaseX | 16 | < 5% |
| Clusterpoint | 10 | < 5% |
| HyperDex | 9 | < 5% |








